Science
-
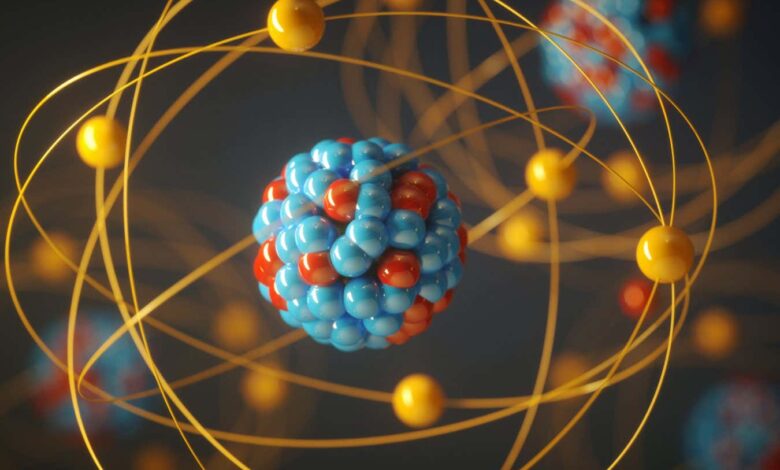
The mystery of nuclear ‘magic numbers’ has finally been resolved
Some atoms seem to be particularly stable because of their numbers of protons and neutrons Shutterstock/ktsdesign A special set of numbers has formed the backbone of nuclear physics research for decades, and now we finally know how it arises from the quantum mix of nuclear particles and forces. Nearly 80 years ago, physicist Maria Goeppert Mayer showed that when the…
Read More » -
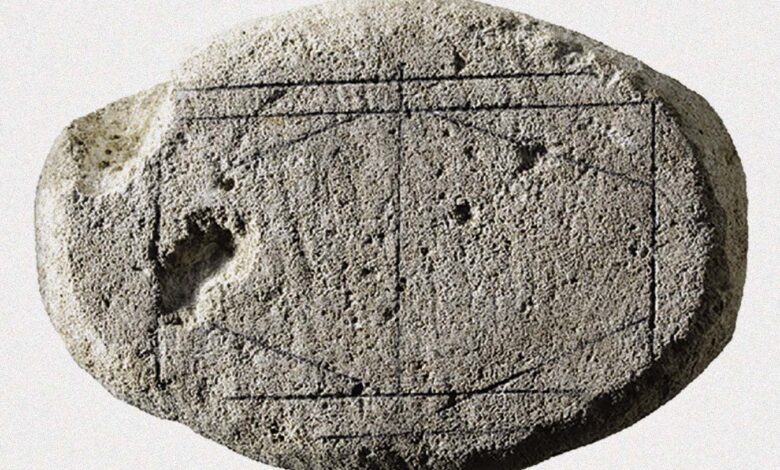

Is this carved rock an ancient Roman board game?
The possible game board with pencil marks highlighting the incised lines Het Romeins Museum A mysterious flat stone with a geometric pattern of straight lines carved into it may be a previously unknown Roman board game. Thousands of simulations by artificial intelligence of how sliding stone or glass pieces could have marked the surface suggest it was an early example…
Read More » -

Ants attack their nest-mates because pollution changes their smell
Harvester ants attack nest-mates whose scent they don’t recognise JorgeOrtiz_1976/Shutterstock Common air pollutants like ozone and nitric oxide can change the way ants smell, prompting their nest-mates to attack them as if they were intruders. Ants recognise their comrades by scent, and when they encounter an ant whose smell they don’t recognise, they respond aggressively, biting and sometimes killing the…
Read More » -

Stick shaped by ancient humans is the oldest known wooden tool
Artist’s reconstruction of a Palaeolithic woman making a digging stick from an alder tree trunk G. Prieto; K. Harvati The oldest known wooden tools have been found in an opencast mine in Greece. They are 430,000 years old and were made by an unidentified species of ancient human – perhaps the ancestors of Neanderthals. Prehistoric wooden artefacts are “very scarce”,…
Read More » -
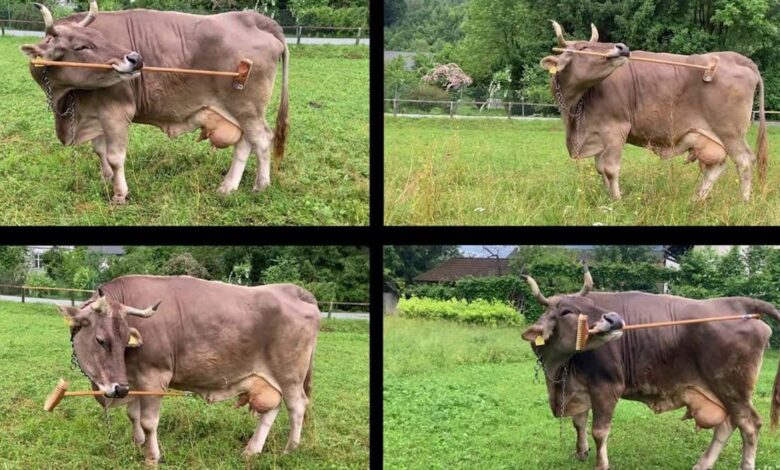

Why a tool-using cow could change how we see farm animals
Veronika the cow is the first recorded non-primate mammal to demonstrate flexible, multi-purpose tool use Antonio J. Osuna Mascaró A few years ago, during a taxi ride, the driver described to me how a pig had transformed his life. A childhood with dogs taught him what to expect from animals, yet he was unprepared for the pig he had taken…
Read More » -

Pompeii’s public baths were unhygienic until the Romans took over
The Stabian Baths, one of the bathhouses first built by the Samnites in Pompeii Icas94/De Agostini via Getty Images A trip to Pompeii’s public baths meant taking a dip in water contaminated with sweat and urine – until the Romans took over and sanitation improved. It’s easy to think of ancient Pompeii as a typical Roman city, particularly given that…
Read More » -
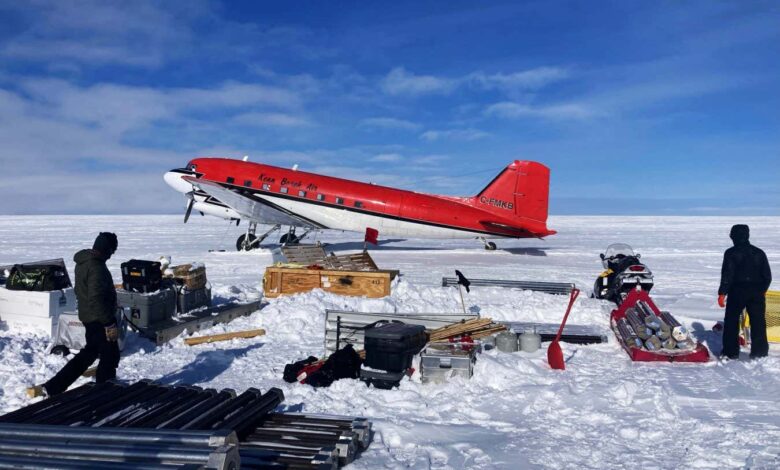

Northern Greenland ice dome melted before and could melt again
Researchers working at Prudhoe Dome in Greenland Caleb K. Walcott-George An ice dome in northern Greenland once melted completely at temperatures the region could experience again this century, a finding that will begin to paint a more accurate picture of how fast the melting Greenland ice sheet could raise global sea levels. Researchers drilled 500 metres down through the centre…
Read More » -

Mathematicians unified key laws of physics in 2025
The equations that govern fluids can be tricky to handle Vladimir Veljanovski / Alamy In 1900, mathematician David Hilbert presented his colleagues with a list of problems he believed both captured the present state of mathematics and the shape of its future. This year, 125 years later, Zaher Hani at the University of Michigan and his colleagues solved one of…
Read More » -

New Scientist changed the UK’s freedom of information laws in 2025
Our successful request for Peter Kyle’s ChatGPT logs stunned observers Tada Images/Victoria Jones/Shutterstock When I fired off an email at the start of 2025, I hadn’t intended to set a legal precedent for how the UK government handles its interactions with AI chatbots, but that is exactly what happened. It all began in January when I read an interview with the…
Read More » -
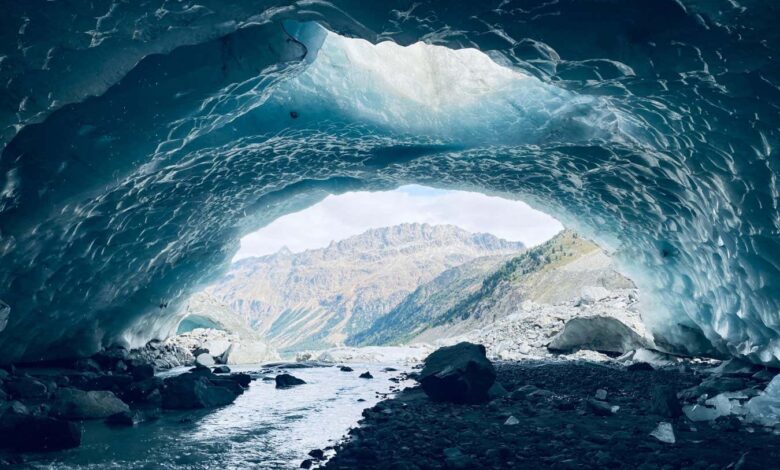

The world will soon be losing 3000 glaciers every year
Meltwater runs through a glacier cave at the front of Morteratsch glacier in Switzerland Lander Van Tricht About 1000 glaciers are now being lost every year and this rate could climb to 3000 per year as soon as 2040, even if countries meet their targets to cut carbon emissions. At least 4000 glaciers have melted away in the past two…
Read More »
